How To Install Cacti On Windows Server 2008 R2
This commodity describes how to monitor Windows machines "private" services such as CPU load, Disk usage, Memory usage, Services, etc. For this, we required to install an NSClient++ addon on the Windows motorcar. The addon acts a proxy between the Windows machine and Nagios and monitors actual services by communicating with the check_nt plugin. The check_nt plugin already installed on the Nagios Monitoring Server, if you lot followed our Nagios installation guide.
We assume that yous've already installed and configured Nagios server according to our post-obit guides.
- How to Install Nagios four.0.1 on RHEL/CentOS 6.x/v.x and Fedora 19/18/17
- Add Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
To monitor Windows Machines y'all will need to follow several steps and they are:
- Install NSClient++ addon on the Windows Auto.
- Configure Nagios Server for monitoring Windows Machine.
- Add new host and service definitions for Windows machine monitoring.
- Restart the Nagios Service.
To make this guide simple and easier, a few of configuration already done for you lot in the Nagios installation.
- A check_nt command definition already added to the control.cfg file. This definition control is used past check_nt plugin to monitor Windows services.
- A windows-server host template already created in the templates.cfg file. This template allows you to add new Windows host definitions.
The above two files "command.cfg" and "templates.cfg" files can be found at /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/ directory. You can alter and add your own definitions that suits your requirement. But, I'd recommend you to follow the instructions described in this commodity and y'all volition exist successfully monitoring your windows host in less than xx minutes.
Step 1: Installing NSClient++ Agent on Windows Machine
Please use the beneath instructions to install NSClient++ Agent on the Remote Windows Host. First download the latest stable version NSClient++ 0.3.1 addon source files, which can be found at below link.
- http://sourceforge.cyberspace/projects/nscplus/
Once you've downloaded latest stable version, unzip the NSClient++ files into a new C:\NSClient++ directory.
Now open up a MS-DOS command prompt from the Starting time Screen –> Run –> type 'cmd' and press enter and change to the C:\NSClient++ directory.
C:\NSClient++
Side by side, register the NSClient++ service on the system with the following command.
nsclient++ /install
Finally, install the NSClient++ systray with the following control.
nsclient++ SysTray
Open the Windows Services Managing director and correct click on NSClient go to Backdrop and then 'Log On' tab and click the check box that says "Permit service to collaborate with the desktop". If it isn't already allowed, please cheque the box to allow information technology to.
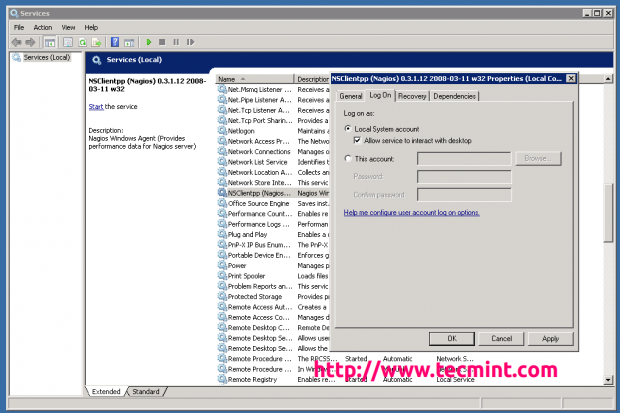
Open NSC.INI file located at C:\NSClient++ directory and uncomment all the modules defined in the "modules" section, except for CheckWMI.dll and RemoteConfiguration.dll.
[modules] ;# NSCLIENT++ MODULES ;# A list with DLLs to load at startup. ; You will demand to enable some of these for NSClient++ to work. ; ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ; * * ; * N O T I C Due east ! ! ! - Y O U H A 5 Due east T O Eastward D I T T H I Southward * ; * * ; ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! FileLogger.dll CheckSystem.dll CheckDisk.dll NSClientListener.dll NRPEListener.dll SysTray.dll CheckEventLog.dll CheckHelpers.dll ;CheckWMI.dll ; ; RemoteConfiguration IS AN EXTREM Early on Thought SO DONT USE FOR Production ENVIROMNEMTS! ;RemoteConfiguration.dll ; NSCA Agent is a new beta module employ with care! ;NSCAAgent.dll ; LUA script module used to write your own "check deamon" (sort of) early beta. ;LUAScript.dll ; Script to bank check external scripts and/or internal aliases, early beta. ;CheckExternalScripts.dll ; Check other hosts through NRPE farthermost beta and probably a fleck dangerous! :) ;NRPEClient.dll
Uncomment the "allowed_hosts" in the "Settings" section and define the IP address of your Nagios Monitoring Server or leave it blank to allow whatsoever hosts to connect.
[Settings] ;# Immune HOST ADDRESSES ; This is a comma-delimited list of IP address of hosts that are allowed to talk to the all daemons. ; If leave this blank anyone can access the deamon remotly (NSClient still requires a valid password). ; The syntax is host or ip/mask so 192.168.0.0/24 will let anyone on that subnet access allowed_hosts=172.16.27.41
Uncomment the "port" in the "NSClient" section and set to default port '12489'. Make certain to open '12489' port on Windows Firewall.
[NSClient] ;# NSCLIENT PORT NUMBER ; This is the port the NSClientListener.dll will mind to. port=12489
Finally showtime the NSClient++ service with the following control.
nsclient++ /start
If your properly installed and configured, y'all should see a new icon in the system tray in xanthous circle with a black 'Grand' inside.
Step ii: Configuring Nagios Server and Add Windows Hosts
At present Login into Nagios Server and add together some object definitions in Nagios configuration files to monitor new Windows auto. Open windows.cfg file for editing with Six editor.
[[email protected]]# vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/windows.cfg
A sample Windows host definition already divers for the Windows machine, you lot can simply change the host definition like host_name, alias, and address fields to appropriate values of your Windows machine.
############################################################################### ############################################################################### # # HOST DEFINITIONS # ############################################################################### ############################################################################### # Ascertain a host for the Windows machine we'll be monitoring # Alter the host_name, allonym, and address to fit your situation define host{ use windows-server ; Inherit default values from a template host_name winserver ; The name nosotros're giving to this host alias My Windows Server ; A longer name associated with the host address 172.31.41.53 ; IP address of the host } Following services are already added and enabled in windows.cfg file. If you wish to add together some more other service definitions that needs to be monitored, you can simple add those definitions to same configuration file. Make sure to modify the host_name for these all services with host_name defined in the above step.
define service{ use generic-service host_name winserver service_description NSClient++ Version check_command check_nt!CLIENTVERSION } Add the post-obit service definition to monitor the uptime of the Windows server. define service{ use generic-service host_name winserver service_description Uptime check_command check_nt!UPTIME } Add together the following service definition to monitor the CPU utilization on the Windows server and generate a Critical warning if the 5-minute CPU load is ninety% or more or a Alarm alert if the v-infinitesimal load is fourscore% or greater. define service{ use generic-service host_name winserver service_description CPU Load check_command check_nt!CPULOAD!-l 5,eighty,ninety } Add the following service definition to monitor retention usage on the Windows server and generate a CRITICAL alert if memory usage is 90% or more or a WARNING alert if retentivity usage is 80% or greater. define service{ use generic-service host_name winserver service_description Memory Usage check_command check_nt!MEMUSE!-w 80 -c 90 } Add the following service definition to monitor usage of the C:\ bulldoze on the Windows server and generate a CRITICAL alert if disk usage is 90% or more or a Alert warning if disk usage is 80% or greater. define service{ utilize generic-service host_name winserver service_description C:\ Drive Space check_command check_nt!USEDDISKSPACE!-fifty c -due west 80 -c xc } Add the post-obit service definition to monitor the W3SVC service state on the Windows machine and generate a Critical warning if the service is stopped. ascertain service{ use generic-service host_name winserver service_description W3SVC check_command check_nt!SERVICESTATE!-d SHOWALL -l W3SVC } Add together the following service definition to monitor the Explorer.exe process on the Windows machine and generate a CRITICAL warning if the process is not running. define service{ use generic-service host_name winserver service_description Explorer check_command check_nt!PROCSTATE!-d SHOWALL -l Explorer.exe } Lastly, uncomment the windows.cfg file in /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg.
[[email protected]]# half-dozen /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
# Definitions for monitoring a Windows car cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/windows.cfg
Finally, verify the Nagios configuration files for any erros.
[[email protected]]# /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -five /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Total Warnings: 0 Full Errors: 0 Things look okay - No serious problems were detected during the pre-flight check
If the verification process throws whatever error messages, fix those errors until the verification process completes without any mistake messages. In one case' you fix those errors, restart the Nagios service.
[[email protected]]# service nagios restart Running configuration check...done. Stopping nagios: washed. Starting nagios: washed.
That's it. Now get to Nagios Monitoring Web interface at "http://Your-server-IP-accost/nagios" or "http://FQDN/nagios" and Provide the username "nagiosadmin" and password. Bank check that the Remote Windows Host was added and is being monitored.
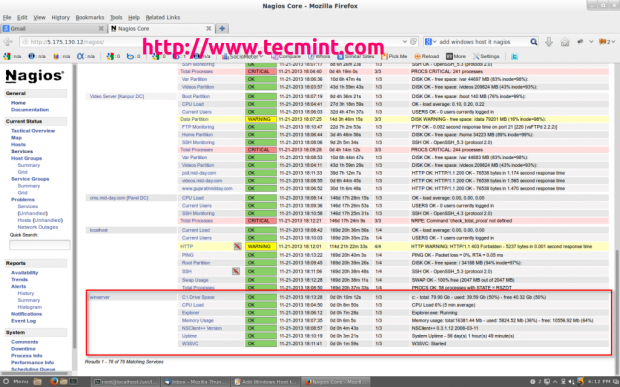
That's information technology! for now, in my up-coming article I will show you how to add together Printer and Switches to Nagios Monitoring Server. If you're having whatever difficulties while calculation Windows host to Nagios. Please do comment your queries via comment section, till then stay tuned to Tecmint.com for more such kind of valuable manufactures.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, Y'all Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you lot are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or ii ) as a token of appreciation.

We are thankful for your never ending support.
Source: https://www.tecmint.com/how-to-add-windows-host-to-nagios-monitoring-server/
Posted by: khanhingall.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Install Cacti On Windows Server 2008 R2"
Post a Comment